Travelling to tropical destinations presents unique challenges for your electronic devices that extend far beyond typical wear and tear. The combination of high humidity, sudden temperature changes, and salt-laden air creates a perfect storm for device malfunction and permanent damage. While you might be focused on capturing memories with your camera or staying connected through your smartphone, the invisible threat of moisture can silently compromise your valuable electronics in ways you might not realise until it’s too late.
Understanding how humidity affects electronic components becomes crucial when venturing into climates where moisture levels consistently exceed 70%. From the rainforests of Southeast Asia to the Caribbean coastlines, these environments pose significant risks to laptops, cameras, tablets, and smartphones. The financial impact of humidity-related damage can be substantial, with repair costs often approaching the price of replacement devices. More importantly, losing access to navigation tools, communication devices, or work equipment whilst travelling can transform an adventure into a logistical nightmare.
Understanding humidity’s impact on electronic device components and circuitry
Moisture infiltration represents one of the most insidious threats to electronic device longevity, particularly in tropical environments where relative humidity frequently exceeds safe operating parameters. When water vapour penetrates device casings, it creates a cascading series of problems that can manifest immediately or develop gradually over weeks and months. The process begins at the molecular level, where moisture molecules interact with various materials and components in ways that compromise electrical conductivity and structural integrity.
Electronic devices typically function optimally within humidity ranges of 30-50% , but tropical climates often maintain levels between 60-90%. This excess moisture doesn’t merely affect surface components; it penetrates through microscopic gaps in device seals, accumulating in areas where it can cause maximum damage. The temperature differentials common in travel situations exacerbate these issues, as devices moved between air-conditioned environments and humid outdoor conditions experience rapid moisture accumulation through condensation.
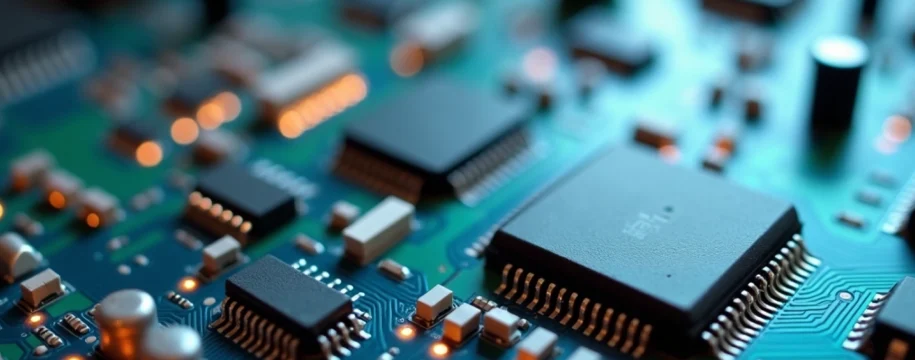
Condensation formation on PCB surfaces and microprocessors
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) serve as the foundation for virtually all modern electronic devices, housing intricate networks of copper traces, resistors, capacitors, and microprocessors. When these components encounter moisture, condensation forms preferentially on metallic surfaces due to their thermal conductivity properties. This phenomenon becomes particularly problematic when devices experience rapid temperature transitions, such as moving from an air-conditioned hotel room to humid outdoor conditions.
Microprocessors generate heat during operation, creating localised temperature gradients that can accelerate condensation formation on surrounding components. The presence of even microscopic water droplets on PCB surfaces can create unintended electrical pathways, leading to short circuits, signal interference, and component failure. Modern smartphones and laptops contain thousands of microscopic components where a single water droplet can bridge connections and cause catastrophic damage.
Corrosion risk assessment for metal contacts and battery terminals
Metal components within electronic devices face immediate and long-term threats from humidity exposure, with corrosion representing the most significant concern for device longevity. Battery terminals, charging ports, and internal connectors contain metals that react readily with moisture, particularly in the presence of trace minerals and salts common in coastal environments. The electrochemical reactions that occur when moisture contacts different metals create galvanic corrosion, accelerating the degradation process.
Gold-plated contacts, whilst more resistant to corrosion than other metals, can still suffer damage when moisture combines with contaminants. The protective gold plating on many connectors measures only a few micrometers thick, making it vulnerable to wear and chemical attack. Battery terminals represent particularly vulnerable points, as the combination of electrical current, metal composition, and moisture creates ideal conditions for rapid corrosion that can render devices completely inoperable.
Hygroscopic material absorption in smartphone and laptop casings
Many modern electronic devices incorporate hygroscopic materials in their construction, substances that naturally absorb moisture from the surrounding atmosphere. These materials, including certain plastics, adhesives, and rubber seals, can absorb significant quantities of water vapour even when devices appear completely dry externally. The absorption process continues as long as environmental humidity exceeds the equilibrium point for these materials.
Smartphone casings often contain multiple hygroscopic components, from rubber gaskets around ports to adhesives securing screen assemblies. As these materials absorb moisture, they can swell slightly, compromising seal integrity and creating pathways for additional moisture ingress. Laptop keyboards represent particularly vulnerable assemblies , with multiple materials that can absorb and retain moisture for extended periods, potentially affecting internal components long after external conditions improve.
Electrolytic capacitor performance degradation in high moisture environments
Electrolytic capacitors, essential components in power supply circuits and signal processing systems, demonstrate particular sensitivity to moisture exposure. These components contain electrolytic solutions that can be contaminated or diluted by absorbed moisture, leading to reduced capacitance values, increased equivalent series resistance, and premature failure. The aluminium oxide dielectric layer within these capacitors can also be compromised by moisture-induced chemical reactions.
Performance degradation in electrolytic capacitors often manifests as reduced device battery life, unstable power delivery, and audio distortion in devices with sound systems. The degradation process accelerates at higher temperatures, making tropical environments particularly challenging for capacitor longevity.
Professional electronics technicians report that humidity-related capacitor failures represent approximately 30% of all electronic device failures in tropical regions.
Pre-travel waterproofing and Moisture-Sealing techniques for consumer electronics
Effective protection against humidity damage begins well before departure, requiring careful planning and implementation of multiple protective strategies. The key lies in creating multiple barriers between your electronic devices and the hostile moisture environment they’ll encounter. Professional-grade protection techniques, originally developed for military and marine applications, have become increasingly accessible to civilian travellers seeking robust device protection.
The most effective approach combines passive protection methods with active moisture management systems. Passive techniques include physical barriers such as waterproof cases and sealing materials, whilst active methods involve moisture-absorbing substances and controlled environments. Successful moisture protection requires understanding that no single method provides complete protection , necessitating layered defence strategies that address different failure modes and exposure scenarios.
Pelican case selection criteria for camera equipment and tablets
Pelican cases represent the gold standard for protective equipment storage, offering exceptional protection against moisture, shock, and temperature extremes. When selecting cases for electronic devices, internal volume efficiency becomes crucial, as excess air space allows for greater humidity fluctuations and condensation formation. The case interior should accommodate the device with minimal extra space whilst allowing for protective foam and desiccant placement.
Case selection criteria should prioritise IP67 or IP68 ratings, indicating complete protection against dust ingress and temporary submersion. Automatic pressure equalisation valves prevent pressure differentials that could compromise case seals whilst maintaining waterproof integrity. Professional photographers working in humid environments typically select cases 20-30% larger than minimum device requirements to accommodate adequate desiccant materials and protective foam whilst maintaining optimal internal atmosphere control.
Silica gel desiccant packet deployment strategies for portable devices
Silica gel desiccants provide cost-effective moisture absorption capabilities when properly deployed and maintained. Standard commercial desiccant packets absorb approximately 40% of their weight in water vapour, but performance varies significantly with temperature and initial moisture content. For tropical travel applications, desiccant quantities should be calculated based on anticipated exposure duration and environmental extremes rather than manufacturer recommendations for temperate conditions.
Effective deployment requires strategic placement within protective cases or device storage areas to maximise moisture absorption efficiency. Desiccant packets should be positioned to create airflow pathways around sensitive device areas whilst avoiding direct contact with device surfaces. Replacement intervals become critical in high-humidity environments, with packets requiring regeneration or replacement every 2-3 days depending on environmental conditions and case opening frequency.
Vacuum sealing methods using ziploc space bags for sensitive components
Vacuum sealing provides an economical method for creating controlled atmospheres around electronic devices during storage and transport. Food-grade vacuum bags offer excellent moisture barrier properties whilst remaining permeable to gases, allowing for pressure equalisation without moisture ingress. The vacuum sealing process removes most atmospheric moisture from the sealed environment, creating conditions where condensation becomes virtually impossible.
Implementation requires careful attention to bag selection and sealing procedures to ensure long-term effectiveness. Multi-layer bags with aluminium barrier films provide superior moisture protection compared to standard plastic bags, though they sacrifice some flexibility and reusability. Devices sealed with adequate desiccant materials can remain protected for weeks even when exposed to extreme humidity conditions, provided the seal integrity remains intact.
Conformal coating application on exposed circuit boards
Conformal coatings represent permanent protection solutions for electronic devices exposed to harsh environmental conditions. These thin polymer films provide moisture barrier properties whilst maintaining electrical insulation and component accessibility. Application requires device disassembly and specialised equipment, making it most suitable for high-value devices or equipment requiring extended tropical deployment.
Several coating types offer different protection characteristics and application requirements. Acrylic coatings provide excellent moisture protection and easy removal, whilst polyurethane coatings offer superior chemical resistance and durability. Silicone-based coatings maintain flexibility across wide temperature ranges but offer reduced chemical resistance. Professional application ensures complete coverage without affecting device functionality or warranty coverage.
Climate-specific protection protocols for southeast asia and caribbean destinations
Different tropical regions present unique challenges for electronic device protection, requiring tailored approaches based on local environmental conditions. Southeast Asian destinations combine high humidity with seasonal monsoons, creating periods of extreme moisture exposure interspersed with intense heat. Caribbean locations add salt spray and constant trade wind exposure to the humidity equation, accelerating corrosion processes and complicating protection strategies.
Regional weather patterns significantly influence protection requirements and strategy effectiveness. Monsoon seasons create periods where traditional protection methods may prove inadequate, necessitating enhanced protection protocols and emergency response procedures.
Environmental monitoring data from tropical research stations indicates humidity levels can fluctuate by 30-40% within a single day during transitional weather periods.
Thailand monsoon season electronics storage solutions
Thailand’s monsoon season presents unique challenges with humidity levels consistently exceeding 85% for weeks at a time. Traditional desiccant materials become quickly saturated under these conditions, requiring frequent replacement or regeneration to maintain effectiveness. Sealed storage solutions must account for the extended duration of extreme conditions rather than brief exposure periods typical in other climates.
Effective storage solutions often incorporate multiple protection layers, including primary device sealing, secondary container protection, and environmental control systems. Professional-grade dehumidification equipment becomes essential for extended stays, particularly for high-value equipment such as cameras and laptops. Local electronics retailers report device failure rates increase by 400% during peak monsoon periods compared to dry season levels, emphasising the importance of proper protection protocols.
Amazon rainforest humidity management for research equipment
Amazon rainforest conditions represent some of the most challenging environments for electronic equipment, with humidity levels consistently above 90% and minimal daily variation. The combination of high humidity, elevated temperatures, and limited infrastructure creates scenarios where equipment failure can have serious safety implications. Protection strategies must account for extended deployment periods without access to replacement equipment or professional repair services.
Research equipment deployment requires ruggedised protection systems capable of maintaining controlled internal environments for weeks or months. Military-specification cases with active dehumidification systems provide the necessary protection levels, though power consumption becomes a limiting factor for portable equipment. Solar-powered dehumidification systems offer sustainable solutions for long-term deployments, utilising renewable energy sources abundant in tropical regions.
Maldives salt air corrosion prevention for marine electronics
Marine environments add salt spray corrosion to humidity challenges, creating accelerated degradation conditions for electronic devices. Salt deposits act as hygroscopic nuclei, attracting and concentrating moisture around sensitive components even when atmospheric humidity appears manageable. The combination of salt and moisture creates highly corrosive conditions that can destroy unprotected electronics within days.
Effective protection requires both moisture exclusion and salt contamination prevention through comprehensive sealing strategies. Regular equipment cleaning becomes essential to remove salt deposits before they can attract sufficient moisture to cause damage. Marine electronics manufacturers typically specify cleaning intervals of 24-48 hours for equipment exposed to salt spray conditions, emphasising the aggressive nature of these environments.
Active moisture control systems and dehumidification technologies
Active moisture control systems provide continuous environmental management capabilities that surpass passive protection methods in challenging conditions. These systems actively remove moisture from enclosed spaces, maintaining optimal humidity levels regardless of external environmental conditions. Modern dehumidification technologies have evolved to provide portable, energy-efficient solutions suitable for travel applications whilst delivering professional-grade moisture control performance.
The effectiveness of active moisture control depends heavily on proper system sizing and deployment strategies. Undersized systems struggle to maintain adequate moisture removal in high-humidity environments, whilst oversized systems consume excessive power and may create overly dry conditions that can damage certain electronic components. Professional installations typically target humidity levels between 35-45% to optimise both component protection and energy efficiency.
Portable dehumidification systems designed for travel applications incorporate advanced moisture removal technologies in compact packages suitable for hotel rooms and temporary accommodations. Thermoelectric dehumidifiers offer silent operation and low power consumption, though their capacity limitations restrict their effectiveness in extreme conditions. Compressor-based systems provide superior moisture removal capabilities but require more space and generate operational noise that may be unsuitable for certain applications.
Integration with protective storage systems multiplies the effectiveness of active moisture control by creating controlled microclimates around specific devices. Pelican cases modified with integrated dehumidification systems maintain optimal internal conditions whilst providing physical protection against impacts and environmental hazards. These hybrid systems represent the current state-of-the-art for high-value equipment protection in extreme environments.
Emergency damage assessment and field recovery procedures for Water-Exposed devices
Despite comprehensive protection measures, moisture exposure incidents can occur through equipment failure, user error, or extreme environmental conditions. Immediate response procedures significantly influence recovery success rates, with actions taken within the first few minutes often determining whether devices can be salvaged. Professional recovery techniques developed for marine and military applications provide proven methodologies for maximising recovery success in field conditions.
The critical window for successful recovery typically spans 30-60 minutes following moisture exposure, during which immediate actions can prevent permanent damage to sensitive components. Power isolation represents the highest priority, as energised circuits in the presence of moisture create conditions for immediate and catastrophic component failure. Statistics from professional recovery services indicate that devices powered off within 2 minutes of water exposure show 80% higher recovery rates compared to devices that remain energised.
Field assessment procedures require systematic evaluation of moisture penetration extent and component vulnerability. Visual inspection provides initial damage assessment, though moisture may penetrate internal areas without obvious external indicators. Operational testing should be avoided until thorough drying procedures have been completed, as premature power application can convert recoverable damage into permanent failure.
Drying procedures must address both surface moisture and absorbed moisture within device materials and components. Ambient air drying proves inadequate for thorough moisture removal, particularly from hygroscopic materials and enclosed spaces within device assemblies. Professional drying techniques utilise controlled temperature and airflow to accelerate moisture removal whilst avoiding thermal damage to sensitive components. Desiccant materials play crucial roles in creating moisture-absorbing environments that extract residual moisture from device interiors.
Component-specific recovery procedures address the unique requirements of different device types and technologies. Lithium-ion batteries require immediate disconnection and specialised handling procedures to prevent thermal runaway conditions that could result in fire or explosion. LCD screens and OLED displays need careful moisture extraction from between panel layers, often requiring professional disassembly for complete recovery. Storage devices may retain data accessibility even when other device functions are compromised, making data recovery a priority consideration in recovery planning.
Insurance considerations and travel electronics coverage for Humidity-Related damage
Insurance coverage for electronic devices during international travel presents complex considerations, particularly regarding humidity-related damage claims. Standard travel insurance policies often exclude coverage for gradual deterioration or damage resulting from environmental exposure, categorising humidity damage as maintenance issues rather than covered incidents. Understanding policy limitations and exclusions becomes essential for travellers carrying valuable electronic equipment to tropical destinations.
Specialised electronics insurance policies provide more comprehensive coverage for environmental damage, though premiums reflect the increased risk associated with tropical travel. These policies typically require detailed equipment documentation, including serial numbers, purchase receipts, and condition assessments prior to departure.
Claims data from major travel insurers shows humidity-related electronic damage accounts for approximately 15% of all travel insurance claims in tropical destinations.
Documentation requirements for successful claims submission extend beyond basic purchase receipts to include detailed damage assessments and professional repair estimates. Photographic evidence of device condition before and after exposure incidents strengthens claim validity, though obtaining such documentation in field conditions can prove challenging. Professional assessment reports from authorised service centres carry
significant weight in determining claim legitimacy, making prompt professional assessment critical for successful coverage outcomes. Travel documentation should include timestamped photographs of equipment condition upon departure and arrival, creating an audit trail that supports environmental exposure claims.
Policy comparison becomes essential when selecting appropriate coverage for high-value electronics travelling to humid environments. Standard homeowners’ insurance extensions may provide limited coverage for personal property during travel, but rarely include environmental damage provisions. Specialised travel electronics insurance offers broader coverage scope but requires careful evaluation of deductibles, coverage limits, and exclusion clauses that may impact claim viability.
Professional photographers and researchers working in tropical environments often invest in comprehensive equipment insurance that covers environmental damage, replacement costs, and business interruption expenses. These policies typically require detailed equipment inventories, regular condition assessments, and adherence to specified protection protocols to maintain coverage validity.
Pre-travel preparation for insurance coverage should include detailed equipment documentation, professional condition assessments, and clear understanding of policy requirements and limitations. Many insurers offer discounted premiums for equipment protected using approved methods and cases, recognising the reduced risk associated with proper protection protocols. Understanding these requirements before departure enables travellers to implement appropriate protection measures whilst ensuring full coverage compliance.
Claims processing for humidity-related damage often involves complex technical assessments to determine whether damage resulted from covered incidents or gradual environmental exposure. Professional damage assessment services provide detailed technical reports that clearly document cause and extent of damage, supporting successful claim resolution. The investment in professional assessment typically represents a fraction of potential equipment replacement costs, making it a worthwhile consideration for high-value electronics.
International travel adds additional complexity to insurance coverage, with policy validity varying by destination country and local regulations. Some insurers require notification for travel to specific high-risk destinations, whilst others automatically exclude coverage for certain geographic regions during particular seasons. Understanding these geographical and temporal limitations prevents unpleasant surprises when filing claims from tropical destinations where humidity damage is most likely to occur.